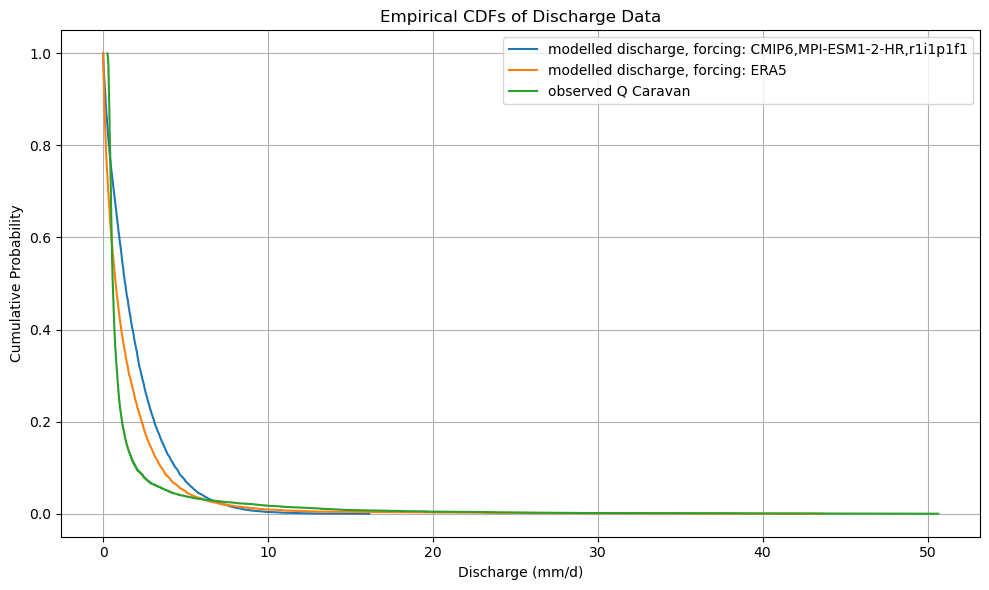
CDF comparison of ERA5 and CMIP model outputs#
by sorting the output in order of decreasing discharge, we can easily make a cummalative distribution. By taking the difference of these functions we derive a (very simple) bias correction function that can later be used to bias-correct the future model output when forced with CMIP projections.
# General python
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore", category=UserWarning)
import numpy as np
from pathlib import Path
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import xarray as xr
import json
# Niceties
from rich import print
# General eWaterCycle
import ewatercycle
import ewatercycle.forcing
# For MEV
from scipy.stats import genextreme, gumbel_r, weibull_min
# Parameters
region_id = None
settings_path = "settings.json"
# Parameters
region_id = "hysets_07377000"
settings_path = "regions/hysets_07377000/settings.json"
# Load settings
# Read from the JSON file
with open(settings_path, "r") as json_file:
settings = json.load(json_file)
display(settings)
{'caravan_id': 'hysets_07377000',
'calibration_start_date': '1994-08-01T00:00:00Z',
'calibration_end_date': '2004-07-31T00:00:00Z',
'validation_start_date': '2004-08-01T00:00:00Z',
'validation_end_date': '2014-07-31T00:00:00Z',
'future_start_date': '2029-08-01T00:00:00Z',
'future_end_date': '2049-08-31T00:00:00Z',
'CMIP_info': {'dataset': ['MPI-ESM1-2-HR'],
'ensembles': ['r1i1p1f1'],
'experiments': ['historical', 'ssp126', 'ssp245', 'ssp370', 'ssp585'],
'project': 'CMIP6',
'frequency': 'day',
'grid': 'gn',
'variables': ['pr', 'tas', 'rsds']},
'base_path': '/gpfs/scratch1/shared/mmelotto/ewatercycleClimateImpact/HBV',
'path_caravan': '/gpfs/scratch1/shared/mmelotto/ewatercycleClimateImpact/HBV/forcing_data/hysets_07377000/caravan',
'path_ERA5': '/gpfs/scratch1/shared/mmelotto/ewatercycleClimateImpact/HBV/forcing_data/hysets_07377000/ERA5',
'path_CMIP6': '/gpfs/scratch1/shared/mmelotto/ewatercycleClimateImpact/HBV/forcing_data/hysets_07377000/CMIP6',
'path_output': '/gpfs/scratch1/shared/mmelotto/ewatercycleClimateImpact/HBV/output_data/hysets_07377000',
'path_shape': '/gpfs/scratch1/shared/mmelotto/ewatercycleClimateImpact/HBV/forcing_data/hysets_07377000/caravan/hysets_07377000.shp',
'downloads': '/gpfs/scratch1/shared/mmelotto/ewatercycleClimateImpact/HBV/downloads/hysets_07377000'}
# Open the output of the historic model and CMIP runs
xr_historic = xr.open_dataset(Path(settings['path_output']) / (settings['caravan_id'] + '_historic_output.nc'))
print(xr_historic)
<xarray.Dataset> Size: 205kB Dimensions: (time: 7305) Coordinates: * time (time) datetime64[ns] 58kB ... Data variables: modelled discharge, forcing: CMIP6,MPI-ESM1-2-HR,r1i1p1f1 (time) float64 58kB ... modelled discharge, forcing: ERA5 (time) float64 58kB ... observed Q Caravan (time) float32 29kB ... Attributes: units: mm/d
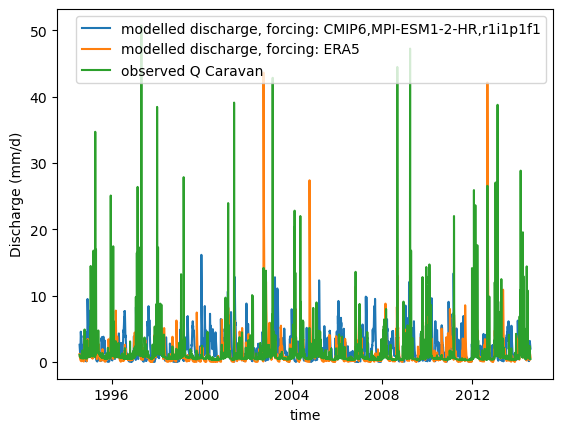
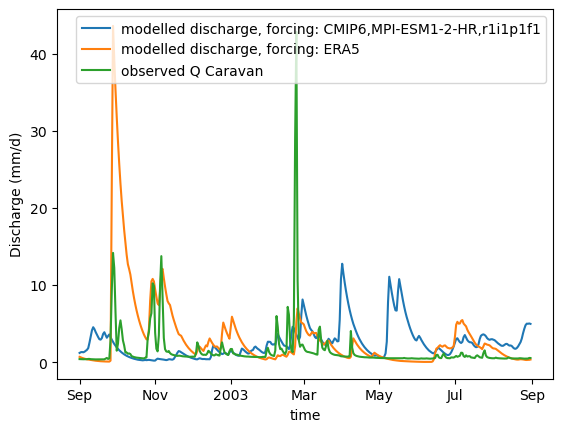
def plot_hydrograph(data_array):
plt.figure()
for name, da in data_array.data_vars.items():
data_array[name].plot(label = name)
plt.ylabel("Discharge (mm/d)")
plt.legend()
xr_one_year = xr_historic.sel(time=slice('2002-09-01', '2003-08-31'))
plot_hydrograph(xr_historic)
plot_hydrograph(xr_one_year)
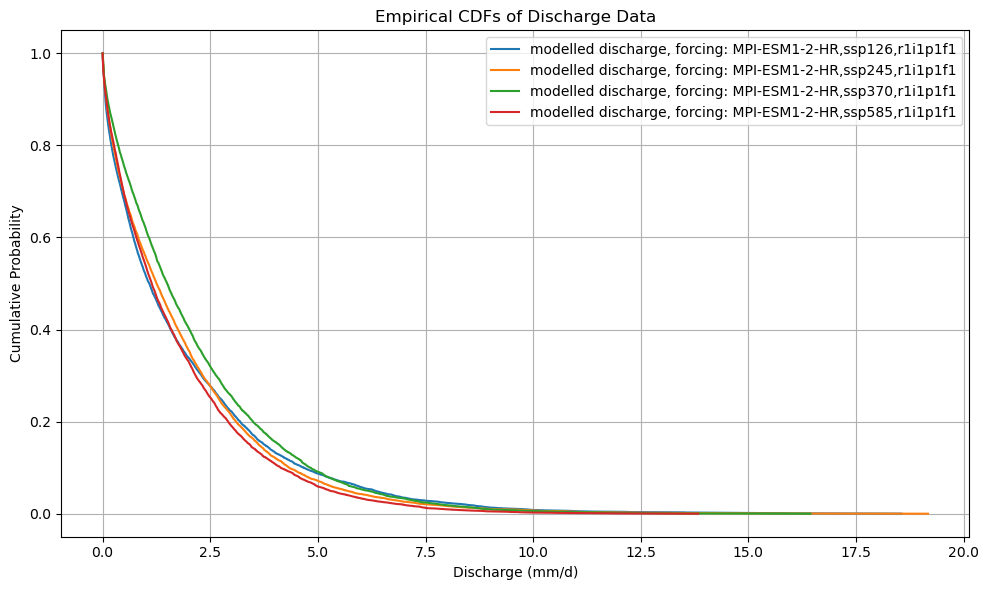
def plot_cdf(ds):
"""
plot cdf for all data variables
Parameters:
- ds: xarray.Dataset
defaults to True
Returns:
- nothing
"""
# 1. Drop time points with missing data in any variable
valid_ds = ds.dropna(dim="time")
# 2. Sort each variable from highest to lowest
sorted_vars = {
name: np.sort(valid_ds[name].values)[::-1] # sort descending
for name in valid_ds.data_vars
}
# 3. Create new indices
n = len(valid_ds.time)
cdf_index = np.linspace(0, 1, n)
return_period_days = np.linspace(n, 1, n)
return_period_years = return_period_days / 365.25 # convert to years
# 4. Construct new xarray Dataset for CDFs
cdf_ds = xr.Dataset(
{
name: ("cdf", sorted_vars[name])
for name in sorted_vars
},
coords={
"cdf": cdf_index,
"return_period": ("cdf", return_period_years)
}
)
# 5. Plot the CDFs
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
for name in cdf_ds.data_vars:
plt.plot(cdf_ds[name], cdf_ds.cdf, label=name)
plt.ylabel("Cumulative Probability")
plt.xlabel("Discharge (mm/d)")
plt.title("Empirical CDFs of Discharge Data")
plt.legend()
plt.grid(True)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
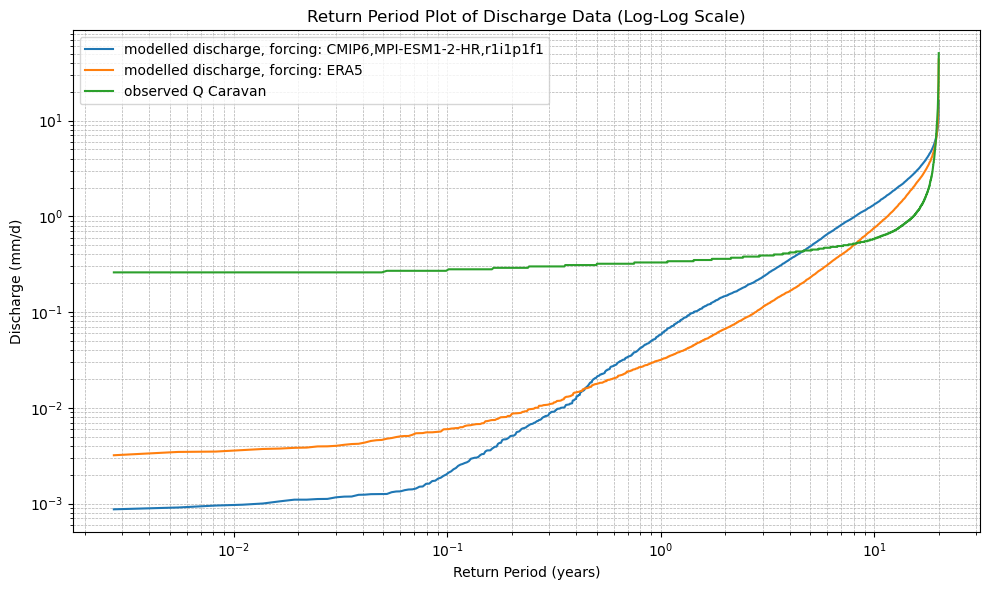
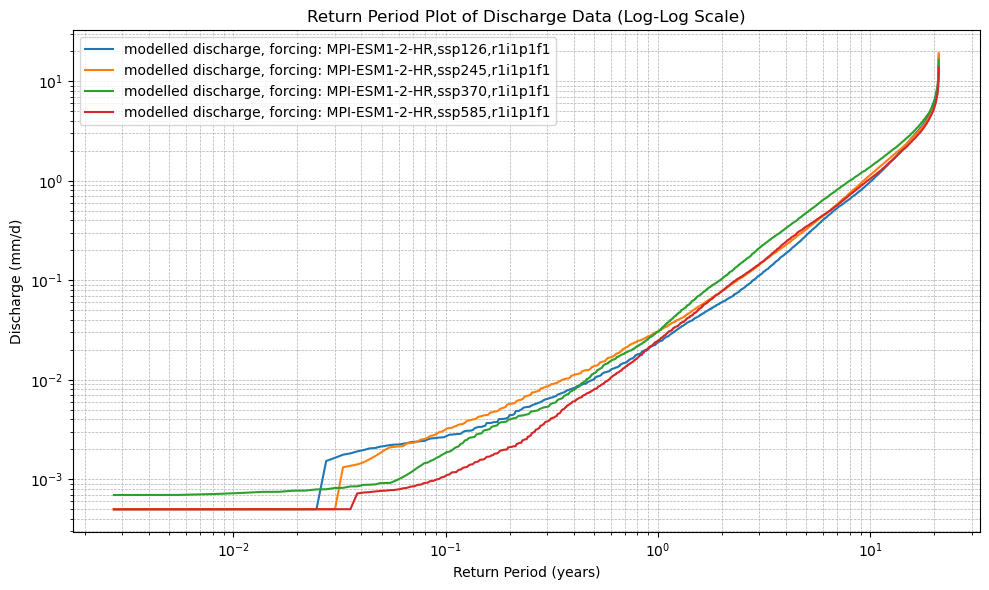
# 6. Plot the Return Period curves (log-log scale)
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
for name in cdf_ds.data_vars:
plt.plot(cdf_ds.return_period, cdf_ds[name], label=name)
plt.xscale("log")
plt.yscale("log")
plt.xlabel("Return Period (years)")
plt.ylabel("Discharge (mm/d)")
plt.title("Return Period Plot of Discharge Data (Log-Log Scale)")
plt.legend()
plt.grid(True, which="both", linestyle="--", linewidth=0.5)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
plot_cdf(xr_historic)
def calculate_mev(ds, dist_type='gev'):
"""
Calculate MEV-based return periods for all data variables in an xarray.Dataset.
Parameters:
- ds: xarray.Dataset
- dist_type: str, one of ['gev', 'gumbel', 'weibull']
Returns:
- xarray.Dataset with MEV return periods
"""
# Step 1: Drop time points with missing data in any variable
valid_ds = ds.dropna(dim="time", how="any")
# Step 2: Extract daily values for each year
years = np.unique(valid_ds['time.year'].values)
mev_distributions = {}
for var in ds.data_vars:
annual_params = []
for year in years:
values = valid_ds[var].sel(time=str(year)).values
if len(values) > 0:
# Fit distribution based on dist_type
if dist_type == 'gev':
params = genextreme.fit(values)
dist_func = genextreme
elif dist_type == 'gumbel':
params = gumbel_r.fit(values)
dist_func = gumbel_r
elif dist_type == 'weibull':
params = weibull_min.fit(values)
dist_func = weibull_min
else:
raise ValueError("dist_type must be one of ['gev', 'gumbel', 'weibull']")
annual_params.append(params)
# Generate MEV by averaging annual distributions
x_vals = np.linspace(np.min(valid_ds[var]), np.max(valid_ds[var]), 1000)
cdfs = [dist_func.cdf(x_vals, *params) for params in annual_params]
mean_cdf = np.mean(cdfs, axis=0)
return_period = 1 / (1 - mean_cdf)
mev_distributions[var] = (x_vals, return_period)
# Step 3: Create MEV xarray Dataset
mev_ds = xr.Dataset(
{
var: ("x", mev_distributions[var][1])
for var in mev_distributions
},
coords={
"x": list(mev_distributions.values())[0][0],
},
attrs=ds.attrs # retain metadata
)
return mev_ds
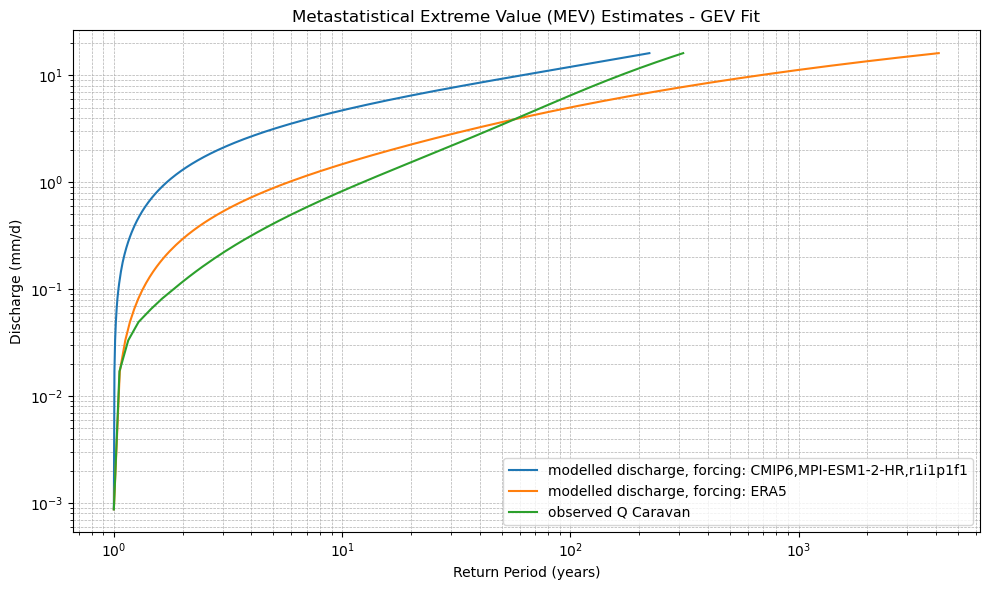
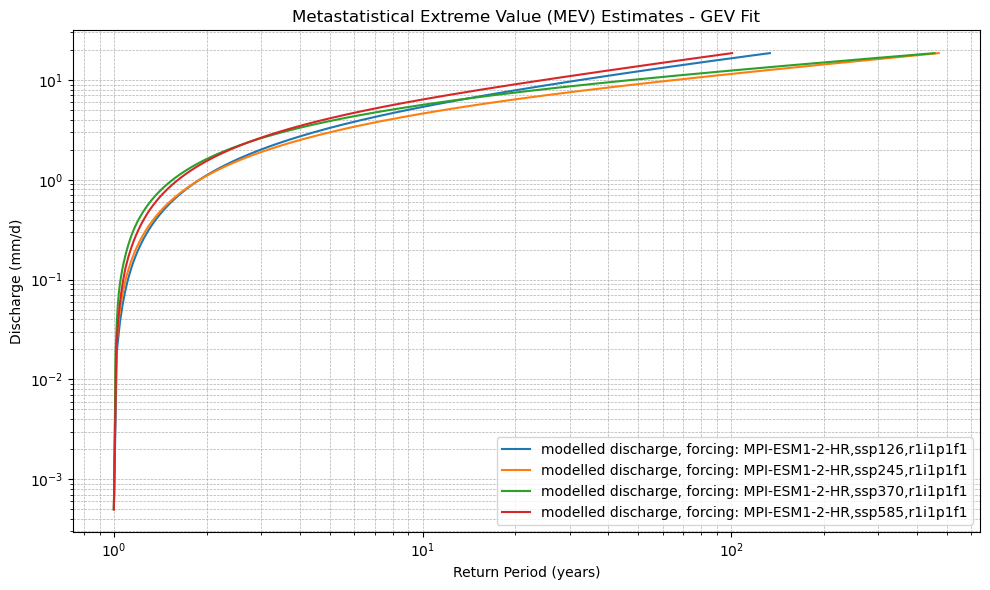
def plot_mev(*mev_datasets, dist_type='gev', labels=None):
"""
Plot MEV curves from one or more xarray.Dataset objects created by calculate_mev().
Parameters:
- mev_datasets: one or more xarray.Dataset objects
- dist_type: str, name of the distribution used (for plot title)
- labels: list of str, labels for each dataset
"""
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
for i, mev_ds in enumerate(mev_datasets):
prefix = f"{labels[i]} - " if labels else ""
for var in mev_ds.data_vars:
plt.plot(mev_ds[var].values, mev_ds['x'].values, label=f"{prefix}{var}")
plt.xscale("log")
plt.yscale("log")
plt.xlabel("Return Period (years)")
plt.ylabel("Discharge (mm/d)")
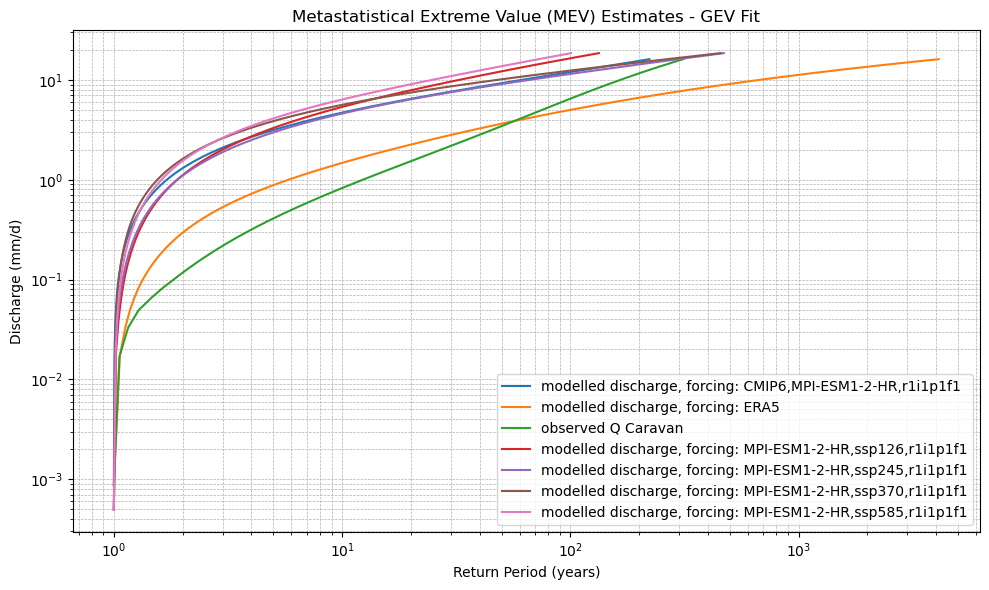
plt.title(f"Metastatistical Extreme Value (MEV) Estimates - {dist_type.upper()} Fit")
plt.legend()
plt.grid(True, which="both", linestyle="--", linewidth=0.5)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
xr_mev_historic = calculate_mev(xr_historic,'weibull')
plot_mev(xr_mev_historic)
# Open the output of the historic model and CMIP runs
xr_future = xr.open_dataset(Path(settings['path_output']) / (settings['caravan_id'] + '_future_output.nc'))
plot_cdf(xr_future)
xr_mev_future = calculate_mev(xr_future,'weibull')
plot_mev(xr_mev_future)
plot_mev(xr_mev_historic, xr_mev_future)